In the ever-evolving landscape of modern medicine, one principle remains timeless and universally valuable: prevention is better than cure. Preventive care, often overlooked in the rush to treat illnesses, plays a vital role in promoting longevity, reducing healthcare costs, and improving overall quality of life. Rather than waiting for symptoms to emerge, preventive care focuses on maintaining health, identifying risks early, and intervening before problems become serious.
What Is Preventive Care?
Preventive care encompasses a broad range of health services that are designed to detect, prevent, and monitor potential health issues. It includes:
Routine check-ups and physical exams
Vaccinations and immunizations
Screenings for conditions like cancer, diabetes, and hypertension
Lifestyle counseling (e.g., nutrition, smoking cessation, stress management)
Monitoring and managing risk factors like obesity, cholesterol, or family medical history
By addressing these areas proactively, individuals can reduce their chances of developing chronic diseases or catching them early when they’re easier—and less costly—to treat.
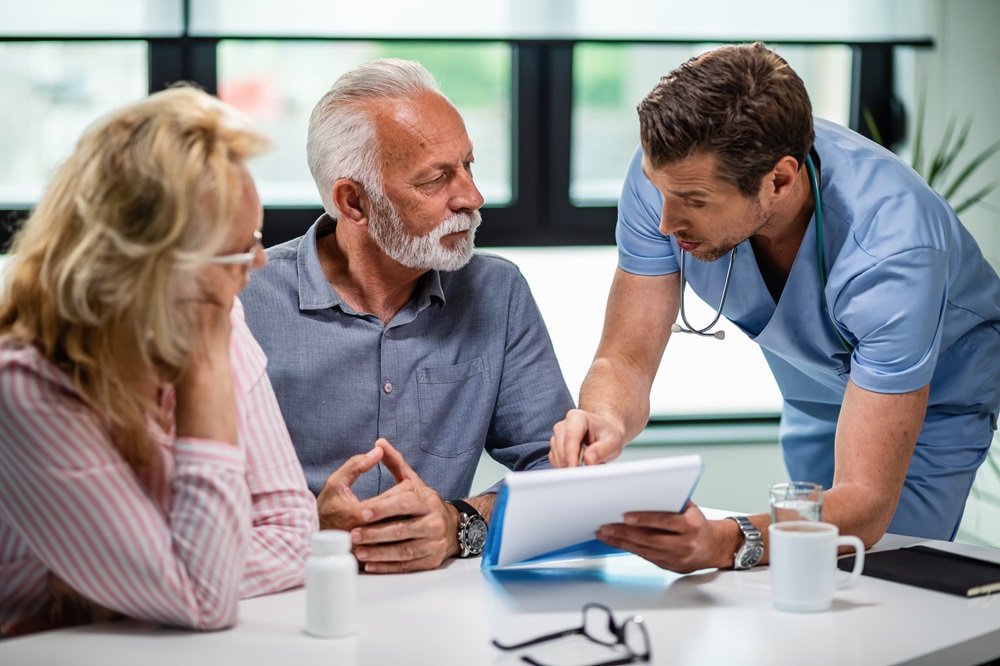

How Preventive Care Supports Longevity
Early Detection Saves Lives
Conditions like cancer, heart disease, and diabetes often develop silently. Regular screenings can detect these diseases in their early stages, significantly improving outcomes. For example, colon cancer screening can reduce mortality by catching pre-cancerous polyps before they turn malignant.Vaccinations Prevent Deadly Diseases
Immunizations have dramatically decreased the prevalence of diseases like measles, hepatitis, and influenza. In older adults, vaccines for pneumonia and shingles can prevent complications that might otherwise lead to hospitalization or death.Management of Chronic Conditions
Preventive care helps manage risk factors such as high blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels. Timely intervention slows the progression of chronic illnesses, preventing complications such as stroke, kidney failure, or heart attack.Mental Health Monitoring
Mental well-being is essential to overall health. Preventive care includes screening for depression, anxiety, and substance abuse—conditions that, when untreated, can diminish both the quality and length of life.
Economic and Social Benefits
Preventive care isn’t just good for your health—it’s good for your wallet and society. Studies have shown that every dollar spent on preventive services can save multiple dollars in future medical treatment. Early intervention minimizes emergency room visits, reduces hospital admissions, and lessens the financial burden on healthcare systems.
Moreover, healthy individuals are more productive, take fewer sick days, and lead more fulfilling lives. When communities prioritize preventive health, everyone benefits.
Preventive Care Across Life Stages
Children: Regular pediatric check-ups, developmental screenings, and immunizations lay a strong foundation.
Adults: Screenings for cancers, heart disease, and metabolic conditions become crucial.
Older Adults: Bone density tests, vision and hearing assessments, and fall prevention strategies are key.
Each stage of life presents new health challenges, and preventive care evolves to meet them.
Taking Action: How to Prioritize Preventive Care
Schedule annual wellness exams.
Keep up-to-date with vaccinations and recommended screenings.
Adopt a healthy lifestyle: eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, avoid smoking, and limit alcohol.
Talk openly with your doctor about family history and personal risk factors.
Don’t ignore mental health—seek help when needed.
Conclusion
Preventive care is not just a healthcare strategy—it’s a life strategy. By staying ahead of potential health issues, individuals can enjoy a longer, more active, and fulfilling life. As healthcare continues to shift from treatment to prevention, embracing this proactive approach is the key to a healthier future for individuals, families, and communities alike.



Pingback: How Wearable Tech Is Becoming Your 24/7 Health Partner – SuperfitLife
Pingback: 10 Proven Habits for a Healthier Lifestyle in 30 Days - SuperfitLife